Current Affairs Section
Indian Scientists Simulate the Mpemba Effect Using Supercomputers / ਭਾਰਤੀ ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀ ਸੁਪਰ ਕੰਪਿਊਟਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਐਮਪੇਂਬਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਦੀ ਨਕਲ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ
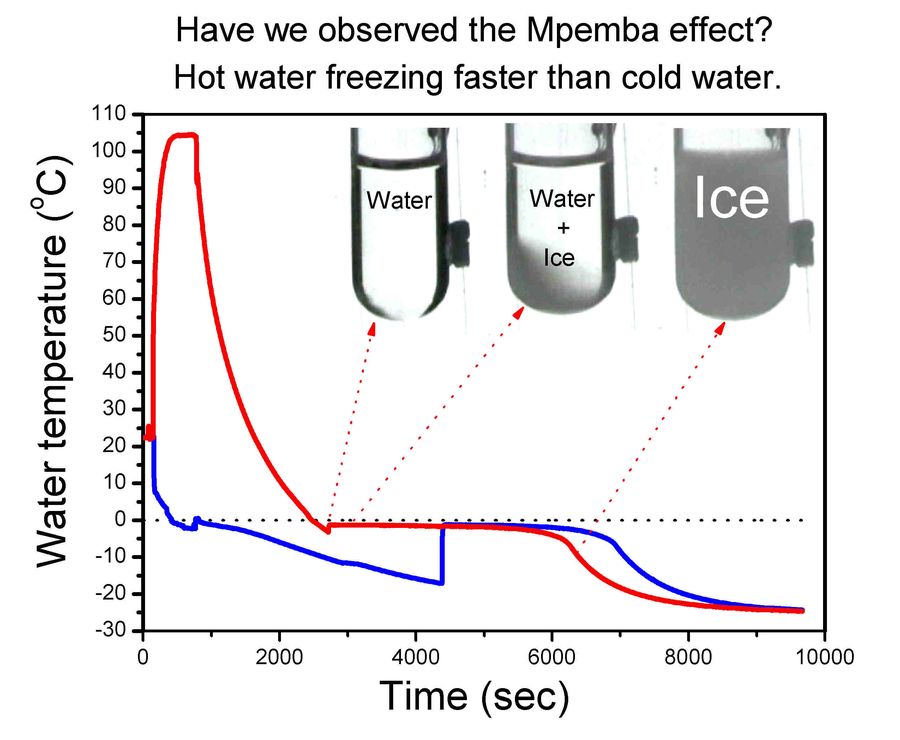
- Indian scientists have developed the first supercomputer-powered simulation that successfully captures the Mpemba effect, helping resolve a long-standing scientific paradox in which hot water freezes faster than cold water under certain conditions.
- The Mpemba effect is a counterintuitive physical phenomenon observed during freezing experiments, influenced by factors such as evaporation, convection, and temperature gradients.
- The effect is named after Erasto Mpemba, who scientifically reported it in 1969, although similar observations were earlier mentioned by Aristotle, Francis Bacon, and René Descartes.
- ਭਾਰਤੀ ਵਿਗਿਆਨੀਆਂ ਨੇ ਪਹਿਲਾ ਸੁਪਰ ਕੰਪਿਊਟਰ-ਸੰਚਾਲਿਤ ਸਿਮੂਲੇਸ਼ਨ ਵਿਕਸਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਐਮਪੇਂਬਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਨੂੰ ਸਫਲਤਾਪੂਰਵਕ ਹਾਸਲ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਇੱਕ ਲੰਬੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਤੋਂ ਚੱਲ ਰਹੇ ਵਿਗਿਆਨਕ ਵਿਰੋਧਾਭਾਸ ਨੂੰ ਹੱਲ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਮਦਦ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਗਰਮ ਪਾਣੀ ਕੁਝ ਸਥਿਤੀਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਠੰਡੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਜੰਮ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ।
- ਐਮਪੇਂਬਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਇੱਕ ਵਿਰੋਧੀ ਭੌਤਿਕ ਵਰਤਾਰਾ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਫ੍ਰੀਜ਼ਿੰਗ ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗਾਂ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਕਿ ਵਾਸ਼ਪੀਕਰਨ, ਸੰਚਾਲਨ ਅਤੇ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਗਰੇਡੀਐਂਟ ਵਰਗੇ ਕਾਰਕਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਿਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ।
- ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਦਾ ਨਾਮ ਇਰਾਸਟੋ ਐਮਪੇਂਬਾ ਦੇ ਨਾਮ 'ਤੇ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸਨੇ 1969 ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਗਿਆਨਕ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਇਸਦੀ ਰਿਪੋਰਟ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਸ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਿਰੀਖਣਾਂ ਦਾ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਅਰਸਤੂ, ਫਰਾਂਸਿਸ ਬੇਕਨ ਅਤੇ ਰੇਨੇ ਡੇਕਾਰਟਸ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਜ਼ਿਕਰ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ।
Category: National